 Origins News!
Origins News!
Neanderthal baby attacks evolutionary dogma
Stepping out 29,000 years from the past, a Neanderthal baby has taught evolutionists a thing or two about human origins, and strengthened the case for special creation. In a just published study, scientists extracted Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA from a Neanderthal infant skeleton found in the northern Caucasus near the Black Sea and laid to rest any question of whether Neanderthals could have been our ancestors. A previous study had examined a 397 Two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds.base pair Neanderthal Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA fragment and compared it with a Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequenceof 986 One of the structural components, or building blocks, of DNA and RNA. A nucleotide consists of a base plus a molecule of sugar and one of phosphate.nucleotide pairs from living humans of diverse ethnic backgrounds. The results showed an enormous 26 nucleotide Two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds.base pair difference between the Neanderthal and Human Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA (a 6.5% difference, which is almost as much as the average difference between human Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA and chimpanzee Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA, which is 8.9%). In this region of the Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA, modern humans differ from one another in an average of eight Two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds.base pairs, and those differences were completely independent of the 26 observed for the Neanderthal fossil. In the current study, a 357 Two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds.base pair The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequence of Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA was examined and found to vary from modern human The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequences at 23 bases (6.4%), nineteen of which were identical to those of the first Neanderthal. A summary of the findings of the two studies can be found in the table below:
Sequence Differences Between Modern Humans and Neanderthals Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA
SampleSequence Number (Read Down)
11111111111111111111111111111111111111
66666666666666666666666666666666666666
00001111111111111122222222222222333333
37890011123455688802334455566679124669
78637812899846923993043408612389104253Modern
HumanAATTCCCCGGACTGCAATTCACTGCCACC-CATCCTCC Neanderthal1 GG.CTTTT.ATTC.T.CCCTGT.A.GA.TATGCT.C.. Neanderthal2 .C......ATT.ATCCCCTGT.A.A..TATGCTTC..
The analysis of the infant's Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA was extremely important, since it was dated at 29,000 years ago - only 1000 years before the last Neanderthal disappeared. If Neanderthals and humans had interbred, one should have expected to see this in the last remnants of the Neanderthals. In addition, since the two Neanderthal fossils were separated geographically by over 2,500 km, it shows that Neanderthals were a homogeneous species that was distinct from ancient humans. In fact, the differences in Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequences compared to modern humans were so great that calculations indicated that the last common ancestor between modern humans and Neanderthal must have been at least 365,000-850,000 years ago.
Igor V. Ovchinnikov, I.V., A. Gotherstrom, G. P. Romanovak, V. M. Kharitonov, K. Liden, and W. Goodwin. 2000. Molecular analysis of Neanderthal Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA from the northern Caucasus. Nature 404: 490-493.
One of the two sex chromosomes, carried by males (1 copy) and females (2 copies) in mammals.X chromosome The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequence variability 4 times greater in chimps than humans
Previous studies have shown that the Of or referring to the mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mitochondrial Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA ( Genetic material found in mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for the cell.mtDNA) The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequencesin chimpanzees are more variable than those in humans (1-3). A recent study has examined a 10,154- Two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds.base pair The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequence on the chimpanzee X chromosome and found that The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequence variability is four times greater in chimpanzees than humans (4), indicating a last common ancestor at least three times earlier than humans.
- Gagneux, P. et al. 1999. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96: 5077
- Morin, P. A. et al. 1994. Science 265: 1193.
- Wise, C. A., M. Sraml, D. C. Rubinsztein, S. Easteal. 1997. Mol. Biol. Evol. 14, 707.
- Henrik Kaessmann, H., V. Wiebe, and S. P��bo. 1999. Extensive Nuclear Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA Sequence Diversity Among Chimpanzees. Science 286:1159-1162.
Early Origin of Eukaryotes
Molecular fossils of biological lipids from 2700-million-year-old shales in Pilbara Craton, Australia have demonstrated that Eukaryotes (organisms whose cells contain a nucleus, probably cyanobacteria) arose at least 1 billion years before the first physical fossils indicated their existence. Collaborating evidence includes the presence of the Hamersley Range in Western Australia, which is a 2500 million year old oxidized iron formation, probably formed as the result of activity of early eukaryotes that produced oxygen through photosynthesis.
Brocks, J.J. A.L. Graham, R. Buick, R. E. Summons. 1999. Archean Molecular
Fossils and the Early Rise of Eukaryotes. Science 285: 1033-1036
Knoll, A.H. 1999. A New Molecular Window on Early Life. Science 285:
1025-1026
Nucleic Acid Origins
Molecular biology has progressed enough so that scientists can begin to ask some "why" questions for the basic design of life's genetic code. Their intent is not to look for intelligent design, but to ask why life evolved to use Ribonucleic acid: a chemical that directs the manufacture of proteins and sometimes codes for the genetic material within certain organisms.RNA and Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA instead of some other molecule. Scientists first asked why the Two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds.base pairs were linked together the way there were. Two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds.Base pairs are linked between the 3' and 5' carbons of the ring. When this was changed to the 2' and 5' carbons, base pairing strength decrease markedly and the strand itself was susceptible to hydrolytic cleavage. Scientists then constructed an alternative form of Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA, using a six-membered sugar ring instead of the usual five-membered ribose. They discovered that some of the new " Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA's" exhibited purine-purine pairing (pairing must be complimentary for it to work as a genetic system). Other constructed " Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA's" exhibited reduced A purine base found in DNA and RNA, which pairs with cytosine in both DNA and RNA.guanine- A pyrimidine base found in DNA and RNA, which pairs with guanine in both DNA and RNA.cytosinepairing that was strongly dependent on the The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequence of Two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds.base pairs. All these problems made the alternate " Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA" unacceptable as a genetic system. Next, scientists constructed Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA's using alternate five-ring sugars. These alternate " Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA's" had a much more rigid backbone structure and enhanced base-pair bonding. However, these characteristics prevent these molecules from being a viable alternative to standard Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA.
Albert Eschenmoser, A. 1999. Chemical Etiology of Nucleic Acid Structure. Science 284:2118.
Is It Time to Uproot the Tree of Life?
The above is the title of a recent article in Science. Molecular biology is allowing evolutionists to examine the relatedness of numerous bacterial species, and recent results are nothing less than startling. Darwinian theory requires that all organisms are, ultimately, related to one another. Therefore, the Functional and physical units of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.genes of living species should demonstrate similarity based upon the point at which the species diverged from a common ancestor. Different kinds of Functional and physical units of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.genes (rRNA, in addition to the entire The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequences of a couple dozen species of microorganisms) from the microbial kingdoms have been analyzed in the attempt to provide molecular evidence for macroevolution. An initial publication last year showed that "Comparisons of the All the DNA contained within species of organisms, which includes both the chromosomes within the nucleus and the DNA in mitochondria.genomes then available not only didn't clarify the picture of how life's major groupings evolved, they confused it." Current taxonomy classifies all living organisms into three kingdoms; eubacteria ("common" bacteria), Archaea ("ancient bacteria that are best known for living in extreme environments) and eukaryotes (all other living forms, including us). The current crisis involves the classification of species of eubacteria and Archaea. Some of the data suggest that certain eubacteria are more closely related to Archaea, and that certain Archaea are not related at all. In an examination of 13 fully Determining the order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequenced All the DNA contained within species of organisms, which includes both the chromosomes within the nucleus and the DNA in mitochondria.genomes, including those of bacteria, Archaea, and the eukaryote, yeast, scientists found that each microbe shares between 77% and 17% of its Functional and physical units of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.genes with another organism, with no clear relationships between species. The results are so confused that some researchers are proposing a complete restructuring of the tree of life, including breaking up the Archaea and redistributing them among the eubacteria. Other researchers have suggested that eukaryotes are more primitive than prokaryotes (both eubacteria and Archaea). However, the fossil record does not support such an interpretation (prokaryotes clearly appeared before eukaryotes). Several researchers have blamed The functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.gene transfer between diverse bacterial species, and even The functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.gene transfer between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Many evolutionists are now suggesting that The functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.gene transfers were so common in the past (a convenient non-provable hypothesis) that a tree of life for microbial species can never be discerned from existing species. Such proposals remove evolutionary theory from being tested, and remove it from scientific criticism.
Pennisi, E. 1999. Is It Time to Uproot the Tree of Life? Science 284: 1305-1307.
One dinosaur species found on multiple continents separated by hundreds of miles of ocean!
Scientists have found a dinosaur species, Allosaurus fragilis, dated to have lived in Colorado some 150 million years ago, also lived on the other side of the Atlantic Ocean, in Portugal, at about the same time. The new fossil was discovered by paleontologist Bernardino Perez-Moreno of the Universidad Aut�noma de Madrid and colleagues in 150-million-year-old rock formations in Leira, 155 kilometers north of Lisbon. The skeleton, of a juvenile dino, is incomplete, but has telltale bones such as the pelvis, vertebrae, and fragments of leg bones, including "unmistakable pelvic features unique to A. fragilis." One puzzle is how the Allosaurus wound up on two continents: The supercontinent of Pangea had broken up tens of millions of years earlier, and by 170 million years ago Portugal was separated from North America by a sea hundreds of miles wide. Geologist Alan Smith of Cambridge University, who specializes in reconstructing ancient geography said, "you cannot get rid of the central Atlantic between Africa and America at this time--the evidence is incontrovertible." No reasonable explanations are available from our evolutionist friends. Water wings anybody?
Staff writer. 1999. Random Samples. Science 284: 903.
Martian Microbes - Not Again!
The group that announced the remains of Martian microbes in a Martian meteorite two years ago (which has since been thoroughly discredited scientifically) has announced "possible bacteria" in a second Martian meteorite. According to the prestigious scientific journal Science, "The latest announcement... so far has left colleagues underwhelmed." (Science 283:1841)
Japanese Origins
Data presented at a recent scientific conference in Japan revealed new information about the origins of the Japanese ancestors. Previous studies had suggested that the two people groups, the Jomonese and the Yayoi, who were ancestors of the Japanese had entered the Japanese islands from the South. However, recent Y-chromosome studies suggest that the Yayoi actually entered Japan from the North and spread south as their Functional and physical units of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.genes mixed with those of the Jomonese. It is hypothesized that the Jomonese crossed into Japan 30,000 years ago by a land bridge that existed until 12,000 years ago. The Yayoi likely developed rice paddy agriculture ~8,000 years ago and sailed to the northern islands of Japan ~2,300 years ago.
Native American Origins
New genetic studies (using Y-chromosomes) indicate that up to 85% of all Native Americans come from a common ancestor who lived ~20,000 years ago (95% confidence interval from 13,700 to 58,700 years). These data fit well into the archeological evidence that the first humans settled in the Americas 12,500 years ago after crossing the Bering land bridge that existed shortly before that time. (De Mendoza, D.H. and R. Braginski. 1999. One of the two sex chromosomes that determines maleness in mammals, carried and passed down from males to males.Y Chromosomes point to Native American Adam. Science 283: 1439-1440.)
Humans Really Are Different!
A newly released book, Three Seductive Ideas, by Harvard University psychologist, Jerome Kagan, makes the claim (and backs it up with experimental evidence) that humans are radically different from every other species of life on earth. Dr. Kagan refutes the ideas of evolutionary pyschologists, including "infant determinism" (the idea that all human behavior is set by age 2) hedonism (the idea that all human behavior is motivated by a desire to maximize pleasure and minimize pain), and "abstractionism" (the idea that all human behavior is controlled by a limited set of laws or rules). He points out that men who committed terrible atrocities had loving parents during their childhood years and that "evolutionary arguments are used to cleanse greed, promiscuity, and abuse of stepchildren of moral taint." Instead, Dr. Kagan shows that humans are a special creation, endowed with a spiritual nature, and motivated by a desire to maintain a feeling of virtue, which is unique among sentient animals. He points out that there are no non-human animal models for human pride, shame, and guilt. Humans also appreciate the difference between moral right and wrong. According to Dr. Kagan, "Not even the cleverest ape could be conditioned to be angry upon seeing one animal steal food from another." According to a recent review of the book in Science, "The idea of the duality of human nature (of meaning over and above mechanism, or mind over and above mechanism, of angel over and above beast), and of the remarkable discontinuity of human natuire from everything that came before, is alive and well for Kagan precisely because he has such a high regard for facts." (For a complete review see Shweder, R.A. 1999. Humans Really Are Different. Science 283: 798.)
Species sorting = species extinction
Punctuated equilibrium is dependent upon the accumulation of Permanent structural alterations in DNA, consisting of either substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotide bases.mutations within a large population that gets "sorted" into an isolated small population that interbreeds the new Permanent structural alterations in DNA, consisting of either substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotide bases.mutations. A new study destroys this idea. Instead of becoming a new species, populations that suffer drastic reductions in numbers are characterized by decreased genetic variability and an expression of detrimental Functional and physical units of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.genes. This happens because normally Possessing two different forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent.heterozygous (containing 2 different Variant forms of a gene at a particular locus, or location, on a chromosome.alleles of each gene) individuals become Possessing two identical forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent.homozygous, due to inbreeding. As a result, detrimental, non-expressed, A genetic disorder that appears only in patients who have received two copies of a mutant gene, one from each parent.recessive Functional and physical units of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.genes become Possessing two identical forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent.homozygous and, therefore, are expressed, resulting in a less fit population. The study examined the effect of a 35-year population decline of greater prairie chickens on their fitness and fertility. The results showed that population decline and isolation of the prairie chicken led to decreased genetic variability, reduced egg viability (from near 100% to less than 80%), and a decline of fertility rates (from 93% to 74%). Only after human intervention (which brought in genetically diverse individuals from other areas) did the population begin to recover. This study calls into serious question the punctuated equilibrium concept of species sorting. (Soul�, M.E. and L.S. Mills. November 27, 1998. No need to isolate genetics. Science 282: 1658 and Wetermeirer, R.L., J.D. Brawn, S.A. Simpson, T.L. Esker, R.W. Jansen, J.W. Walk, E.L. Kershner, J.L. Bouzat, and K.N. Paige. November 27, 1998. Tracking the long-term decline and recovery of an isolated population. Science 282: 1695.)
Design of small Organic compounds made of amino acids arranged in a linear chain, joined together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of the adjacent amino acid residues.proteins
Scientists have been attempting to be able to determine a An organic compound made of amino acids arranged in a linear chain, joined together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of the adjacent amino acid residues.protein's native conformation (or folding) by examining the A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. Often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins.amino acid The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequence. Despite years of study, the ability to do this using even the fastest computers is beyond our reach. For example, for a typical 100 A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. Often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins.amino acid An organic compound made of amino acids arranged in a linear chain, joined together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of the adjacent amino acid residues.protein (moderate to small in size) could exist in any of 3200 possible backbone configurations. Using a super fast computer (1015 computations/sec) it would take 1080 seconds, which exceed the age of the universe by a factor of 60 orders of magnitude! This fact alone may give you a better perspective on the mind of God.
Berendsen, H.J.C. 1998. Perspectives: An organic compound made of amino acids arranged in a linear chain, joined together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of the adjacent amino acid residues.Protein Folding. A Glimpse of the Holy Grail? Science 282: 642-643.
Human racial diversity: no clear genetic lines
This story is going to be disconcerting to racists, who pride themselves on "genetic purity." According to geneticists and anthropologists, genetic diversity appears to fall along a continuum, with no clear breaks delineating different racial groups. It will be good to finally do away with physical differences, when we see each other in heaven. "There is neither Jew nor Greek, slave nor free, male nor female, for you are all one in Christ Jesus" (Galatians 3:28).
Marshall, E. 1998. CULTURAL ANTHROPOLOGY: Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA Studies Challenge the Meaning of Race. Science 282: 654-655
Death of the hydrogen-based microbes theory
A number of theories have proposed that hydrogen may supply the energy requirements of microorganisms that have been found living deep within the subsurface of the Earth's crust. Proposals have suggested that such a supply would allow for such lifeforms on other planets and may have accounted for the beginning of life on Earth. However, a recent report demonstrates that no hydrogen is produced from basalt-ground-water interactions at evironmentally relevant pH. By lowering the pH, the authors of the study were able to get transitory hydrogen production, which they concluded, "cannot be sustained over geologically significant time frames."
Anderson, R.T., F.H. Chapelle, and D.R. Lovley. August 14, 1998. Evidence Against Hydrogen-Based Microbial Ecosystems in Basalt Aquifers. Science 281: 976-977.
Sudden appearance of mammals
At the recent meeting of the International Symposium on the Origin of Mammalian Orders, scientists presented evidence testifying of the rapid appearance of mammals in the fossil record during the beginning of the Tertiary period. During the first 16 million years of the Tertiary period, 18 orders of mammals appeared. Many scientist had claimed that gaps in the fossil record could account for the apparent sudden appearance of mammals. However, Dr. David Archibald (San Diego State University), looked at the numbers of fossil site spanning the period of 5 million years before and after the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary. Dr. Archibald found that sampling was equal for periods before and after the boundary, although only 11 genera were found in the 5 million years before the beginning of the Tertiary compared to 139 genera in the 5 million years following. As he stated, "Something happened to cause this explosion of speciation." The results of the fossil record are not confirmed by molecular clocks reported earlier this year. Dr. John Allroy, a paleontologist at the National Museum of Natural History (Washington D.C.) stated, "If molecular analysts can't find evidence of this explosion in speciation, then they don't know anything about the evolutionary process."
Dennis Normile. August 7, 1998. MAMMALIAN EVOLUTION MEETING: New Views of the Origins of Mammals. Science 281: 774 - 775.
Whales lose ancestors?
The discovery of two 50-million-year-old whales from the family Pakicetidae suggest that the previously thought link between the mesonychians and whales seems unlikely, according to Dr. Hans Thewissen (Northeastern Ohio Universities College of Medicine). The fact that these fossils have more primitive teeth than the mesonychians from which they were supposed to have evolved led Dr. Thewissen to conclude that there was "considerable doubt" that cretaceans (whales) are closely related to mesonychians. Paleontologists now are attempting to link whales with the hippopotamus (artiodactyls). However, Dr. Maureen O'Leary (State University of New York) stated, "it's difficult to connect hippos with whales in the fossil record."
Dennis Normile. August 7, 1998. MAMMALIAN EVOLUTION MEETING: New Views of the Origins of Mammals. Science 281: 774 - 775.
No link between ecology and evolution?
Evolutionary theory predicts that ecology should profoundly effect evolution within groups of related species. A recent study examined the ecological dominance of two bryozoan clades (Cyclostomata and Cheilostomata) and how that related to evolutionary success over the last 140 million years. The results indicated that "evolutionary success and ecological dominance can be decoupled and profoundly different, even over tens of millions of years." Previous studies had shown that the Permium and Triassic mass extinctions had removed other byrozoan clades that had much higher ecological diversities (Taylor, P.D., and G.P. Larwood, in Extinction and Survival in the Fossil Record, G.P. Larwood, Ed. (Clarendon, Oxford, 1988), pp. 99-119), which is counterintuitive to evolutionary theories.
McKinney, F.K., S. Lidgard, J.J. Sepkoski, Jr., and P.D. Taylor. August 7, 1998. Decoupled temporal patterns of evolution and ecology in two post paleozoic Clades. Science 281: 807-809.
Missing bird-dinosaur link found?
Archaeopteryx has been described as a link between birds and dinosaurs, although it is remarkably similar to modern birds. Attempts to find more primitive intermediates have been unsuccessful - until now - so say a group of paleontologists (see the July, 1998 issue of National Geographic). The group has found two turkey-sized dinosaurs that have both downy and modern flight feathers on their arms and tail. Their skeletal structure is similar to theropod dinosaurs (short arms - too short to be useful in flight, serrated teeth, theropod-like pelvis, etc.). The conclusions are obvious. Right? However, other researchers dispute the claims. They point to shortened tail and fused sternum, arguing that they are more advanced than Archaeopteryx. These researchers believe that the intermediates are actually flightless birds. Oh, did I mention that the new fossils are dated to have appeared at least 20 million years after the appearance of the first Archaeopteryx? Those little details do get in the way of evolutionary theory, don't they! For more information on some of the controversies, see Demise of the "Birds are Dinosaurs" Theory, located on this site.
Ann Gibbons. June 26, 1998. Dinosaur fossils, in fine feather, show link to birds. Science 280: 2051.
The Human Brain Drain
Modern humans have brain sizes larger than any other placental mammal relative to body size. The human brain uses a tremendous amount of energy - up to 60% of total energy consumed in newborns. A recent study suggests that the large increase in brain size was balanced by a similar reduction in the size of the gastrointestinal tract. However, other mammals, such as pigs, with small intestines don't have brains as large as ours. In addition, the theory doesn't hold for birds or bats. The presence of large brains in humans presents a problem to evolutionists, since it presents a large energy drain upon the species, especially before the advent of agriculture and reliable food supplies.
Ann Gibbons. May 29, 1998. Solving the brain's energy crisis. Science 280: 1345.
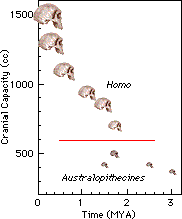 More
(or less) on Brains
More
(or less) on Brains
One of the problems in the theories of human evolution has been the huge difference between the brain capacity of our genus (Homo) and the genus of our supposed ancestors (Australopithecus). A recent discovery of a large Australopithecine skull was anticipated to lessen the gap between the two genera. However, a recent study, using computerized tomography technology has determined that the new skull (Stw 505) has a brain capacity no larger than the size of the largest published value. However, in doing the measurements and checking their validity, the group determined that nearly all of the brain capacities of Australopithecine skulls is inflated. In reality, many Australopithecine skulls have brain capacities no larger than those of chimpanzees. Thus, there exists a huge difference between the brain capacity of the oldest Homo specimen and the largest Australopithecine skull.
Dean Falk. June 12, 1998. Hominid brain evolution: looks can be deceiving. Science
280: 1714.
Conroy, G.C., G.W. Weber, H. Seidler, P.V. Tobias, A. Kane, and B. Brunsden.
1998. Endocranial capacity in an early hominid cranium from Sterkfontein, South
Africa. Science
280: 1730-1731.
The earth's largest extinction (at the end of the Permium period) now appears to have taken place over a period as short as 10,000 years and not millions, as previously thought. During this time nearly 90% of all species became extinct. Even so, life reappeared rapidly after this catastrophic event. The new study examined the ratio of carbon-13 to carbon-14 in the rocks, the layers of which were dated by the uranium-lead method. A rapid shift in carbon-13 to carbon-14 ratio over a short period of time indicated that much of the carbon originally associated with living organisms became part of the inorganic carbon pool for a short period of time associated with the end of the Permium period. A rapid restoration of the carbon-13 to carbon-14 ratio indicates that living organisms rapidly repopulated the earth after this catastrophic extinction event.
Kerr, R. May 15, 1998. Biggest extinction looks catastrophic. Science
280: 1007.
S. A. Bowring, * D. H. Erwin, Y. G. Jin, M. W. Martin, K. Davidek, W. Wang. May
15, 1998. U/Pb Zircon Geochronology and Tempo of the End-Permian Mass
Extinction. Science
280: 1039.
Limits to Evolution
Irreducible complexity is something many evolutionists say does not exist in nature. The "reductionists" believe that there are no limits to an organism's variability and its ability to evolve. However, a new report demonstrates that when three characters are affected by a The functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.gene, the The functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.gene cannot change, but is constrained by the dependency of the other characteristics. Therefore, evolution is now falsifiable if organisms can be found that have broken this principle. In addition, this study demonstrates that the ability of organisms to evolve is limited.
Gunter Wagner. February 20, 1998. EVOLUTION: Complexity Matters Science
279:1158)
and David Waxman, Joel R. Peck. February 20, 1998. Pleiotropy and the
Preservation of Perfection Science
279: 1210.
Molecular Biology has greatly added to our ability to understand the how the cell functions at the molecular level. A recent report used genetic selection and "directed molecular evolution" to redesign a bacterial A protein that encourages a biochemical reaction, usually speeding it up.enzyme (chorismate mutase) from its natural dimeric (2 subunit) structure to a monomeric complexly folded A protein that encourages a biochemical reaction, usually speeding it up.enzyme with nearly identical activity to the natural A protein that encourages a biochemical reaction, usually speeding it up.enzyme. The surprising thing to the researchers was that of all the The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequences they designed, only 0.05% of those redesigned Proteins that encourage a biochemical reactions, usually speeding them up.enzymes expressed appreciable enzymatic activity. What does this tell us? Since evolution is based upon random A permanent structural alteration in DNA, consisting of either a substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotide bases.mutation, the probability of randomly designing this A protein that encourages a biochemical reaction, usually speeding it up.enzyme is extremely unlikely. It is probable that other Proteins that encourage a biochemical reactions, usually speeding them up.enzymes will be designed to similar levels of precision.
MacBeath, G., P. Kast, and D. Hilvert. March 20, 1998. Redesigning A protein that encourages a biochemical reaction, usually speeding it up.enzymetopology by directed evolution. Science 279: 1958.
http://www.godandscience.org/evolution/originnews.html
Last Modified September 21, 2002


