God of the Gaps - Do All Christian Apologetics Fall Into This Kind of Argument?

Introduction
"God of the gaps" refers to the perception that all arguments for the existence of God are the result of gaps in our scientific knowledge. According to this philosophy, the number of gaps should decrease as scientific knowledge expands. Since this knowledge doubles every ten years, we should see these gaps disappearing at an ever increasing rate. Is this is what is happening in all fields of science? This page will examine areas of science commonly cited as supporting the existence of God to see if they fall into an argument of gaps or if these "gaps" are actually increasing in number. Since an increase in the number of gaps would not be predicted by those who claim that these kinds of arguments represent a "God of the gaps" variety, we can determine whether these are merely gaps in knowledge or true evidence for design.
What evidence for God's existence has science eliminated?
There are three major areas that have been posited to provide evidence for the existence of God. Thomas Aquinas, argued in favor of the existence of God on the basis of fundamental aspects of the universe such as causality and change. William Paley argued that the hand of God is evident in the apparent design of the universe and living beings. The third line of evidence argues that God makes Himself evident in personal transcendent experiences of people. Of these three lines of evidence, science has eliminated none, although many would argue that the evidence for biological evolution has weakened the argument for the design of living organisms. Even so, there are numerous gaps in evolution - many of which have appeared recently.
Design in life
Intelligent design in biology
A common complaint against biological intelligent design arguments is that our understanding of the biology is insufficient to answer the question about a mode by which some "irreducibly complex" system might have arisen through an evolutionary process. The most famous example of this kind of argument is the one involving the bacterial flagellum. This biological rotary engine is a complex association of 50 gene products, the absence of any one of which results in an inability of the system to function at all. Although the system is irreducibly complex now, biologist have proposed mechanisms by which the system could have been synthesized from previously existing structures and enzymes. Although these explanations are not likely to account for the actual way such a system might have arisen, it is possible that better explanations could be revealed through a better understanding of the genomics of different species of flagellated bacteria. As such, the "design" of the bacterial flagellum and other "irreducibly complex" systems could represent a gap in our current understanding of the biology and genetics.
Whether of not the bacterial flagellum is designed could be tested by a
further examination of this, and other examples of intelligent design. It would
be expected that very few systems would have arisen through an extremely rare
sequence of evolutionary events (see Michael Behe's book,
The Edge of Evolution: The Search for the Limits of Darwinism![]() ). However, since there are many different
biological systems, one would expect that there would be a few examples
of these kinds of systems. If this represents a true God of the gaps
explanation, it would be expected that few, if any, other such examples would be
found in nature. If many examples are found, it would suggest that some kind of
design might be involved. Time will tell.
). However, since there are many different
biological systems, one would expect that there would be a few examples
of these kinds of systems. If this represents a true God of the gaps
explanation, it would be expected that few, if any, other such examples would be
found in nature. If many examples are found, it would suggest that some kind of
design might be involved. Time will tell.
Junk DNA and pseudogenes

![]() Previously thought to be one of the best arguments against the design
of biological organisms was the existence of large amounts of "junk DNA"
(technically called non-coding DNA) in the genomes of most animals. In fact, it
was originally thought that up to 95% of the human genome did not code for any
kind of RNA or protein product. However, studies over the last 15 years have
virtually destroyed this kind of argument.1 In a remarkable pilot study published by the
ENCODE Project
Consortium, hundreds of scientists analyzed the functionality of 1
percent (30 Mb) of the human genome. Much to
scientists' surprise, the study found that the majority of DNA in the
human genome is transcribed into functional RNA.1 Since most of the DNA
used in the study was chosen randomly, it seems likely that this result will
hold for the entire human genome. So, there is a lot less non-coding DNA in our
genome then was originally assumed. According to a news release from the
Consortium, "This broad pattern of transcription challenges the long-standing
view that the human genome consists of a relatively small set of discrete genes,
along with a vast amount of so-called junk DNA that is not biologically active."2
So, the "gap" that claimed that DNA evolved through extensive instances of gene
duplication and evolution with numerous non-coding failures seems to be wrong.
Score one against "science of the gaps."
Previously thought to be one of the best arguments against the design
of biological organisms was the existence of large amounts of "junk DNA"
(technically called non-coding DNA) in the genomes of most animals. In fact, it
was originally thought that up to 95% of the human genome did not code for any
kind of RNA or protein product. However, studies over the last 15 years have
virtually destroyed this kind of argument.1 In a remarkable pilot study published by the
ENCODE Project
Consortium, hundreds of scientists analyzed the functionality of 1
percent (30 Mb) of the human genome. Much to
scientists' surprise, the study found that the majority of DNA in the
human genome is transcribed into functional RNA.1 Since most of the DNA
used in the study was chosen randomly, it seems likely that this result will
hold for the entire human genome. So, there is a lot less non-coding DNA in our
genome then was originally assumed. According to a news release from the
Consortium, "This broad pattern of transcription challenges the long-standing
view that the human genome consists of a relatively small set of discrete genes,
along with a vast amount of so-called junk DNA that is not biologically active."2
So, the "gap" that claimed that DNA evolved through extensive instances of gene
duplication and evolution with numerous non-coding failures seems to be wrong.
Score one against "science of the gaps."
Related to this argument is a similar one regarding pseudogenes.3 These sequences are hypothesized to represent functional genes that have undergone duplication followed by inactivation through random mutation over time. Many scientists believed that the presence of these "molecular fossils"4 was a sure sign that DNA sequences were not designed. The first functional role for a A sequence of DNA that is very similar to a normal gene but that has been altered so it is not expressed.pseudogene was found in a study that was randomly inserting a fruit fly The functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.gene into the mouse Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA and accidentally produce a lethal mutation.5 It was found that the insertion occurred in the middle of a A sequence of DNA that is very similar to a normal gene but that has been altered so it is not expressed.pseudogene The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequence called Makorin1-p1. Not only was the A sequence of DNA that is very similar to a normal gene but that has been altered so it is not expressed.pseudogene functional, but its destruction resulted in a lethal A permanent structural alteration in DNA, consisting of either a substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotide bases.mutation in the mice. Scientists had found the first required A sequence of DNA that is very similar to a normal gene but that has been altered so it is not expressed.pseudogene. Since this first study, many other studies have found that pseudogenes exhibit functional activity, including gene expression, gene regulation, and generation of genetic diversity.6 Recent work shows that up to 50% of pseudogenes in some genomes appear to be transcriptionally active.7 The ENCODE project pilot study estimated that at least 19% of all pseudogenes are transcribed (admittedly an underestimate).8
Overlapping Genes
When scientists were first sequencing the human genome, they were expecting at least 30% more genes than what were found. It now appears that the genome is encoded in a very concise manner and has been optimized for the minimal length required to do the job. The evidence for the design of DNA is getting stronger - not weaker - as the mysteries of human genome are being revealed. This evidence certainly doesn't seem to fall into a God of the gaps variety.
A surprising discovery in genomics is that transcripts of DNA come from regions that extensively overlap one another. The overlapping sequences that code for these transcripts are often transcribed over different reading frames (the three base codons are offset from each other). This means that any insertion, deletion, or base substitution would impact two transcripts at the same time. In fact, there is at least one example where three transcripts overlap each other. Even more surprising is that there are coding regions that overlap on the opposite "anti-sense" strand of DNA. What this means is that any mutation of overlapping transcripts will simultaneously alter the amino acid sequence in two separate proteins. It is inconceivable to postulate how natural selection could operate on such a system, since it would be extremely unlikely that a mutation would be simultaneously beneficial for both transcripts. Geneticists are puzzled how regions of DNA containing overlapping transcripts could have evolved:
"Similarly, evolutionary origin of such genes is not known, existing hypotheses can explain only selected cases of mammalian gene overlaps which could originate as result of rearrangements, overprinting and/or adoption of signals in the neighboring gene locus."9
Although this particular argument could turn into a God of the gaps type, it is certainly intriguing, and worth watching, especially since molecular biologists admit that there is no viable evolutionary mechanism to explain the vast majority of instances of overlapping genes. The appearance of new "gaps" is not what one would predict from a purely naturalistic perspective as scientists rapidly gain new knowledge of how genetic systems function.
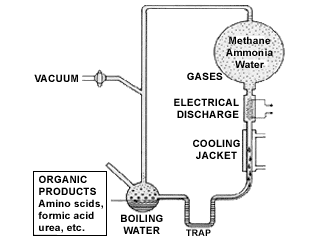
Origin of life
The origin of the first biological organism has been an intense area of study for the past 50 years. Beginning in 1953, when Stanley Miller first demonstrated that mixtures of reducing gases subjected to electrical discharges produced many organic compounds, including several A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. Often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins.amino acids, scientists were confident that the mystery of life's origin would be discovered.10 However, recent studies have revealed what chemistry can and cannot do. In addition, continuing studies in earth and planetary sciences reveal that the atmosphere of the early earth was not reducing, as had been assumed in many prebiotic chemistry experiments (including Miller's). In fact, the presence of oxidized zircons dated at 4.3 billion years ago11 (only 0.25 billion years after earth's creation) tell us that atmospheric conditions were not reducing when life appeared ~3.8 billion years ago.12 Such facts have relegated origin of life hypotheses to hydrothermal oceanic vents, where volcanic outgassing produces reducing conditions. However, since there is no source of electrical discharge undersea, the process is prohibitively inefficient (if it functions at all). The other problem is that many of the critical building blocks of life cannot be synthesized under these conditions. Even if they could appear miraculously, assembly often requires high concentrations, which would not have been available. Although it is possible that such materials could be concentrated by drying on shoreline coastal areas, the simultaneous drying of the salts present in the sea water inhibit virtually all assembly reactions. Additionally, recent studies have show that the polymerization of the molecules necessary for cell membrane assembly cannot occur in sea water,13 which was at least twice as salty as it is now.14 The once highly touted RNA World hypothesis has been seriously challenged, since pyrimidine nucleosides ( A pyrimidine base found in DNA and RNA, which pairs with guanine in both DNA and RNA.cytosine and A pyrimidine base found in RNA, which pairs with the complementary base adenine.uracil) do not form under prebiotic conditions nor are found in carbonaceous meteorites.15 Synthesis of ribose and deoxyribose (the sugars that form the backbone of RNA and DNA) is extremely inefficient (and unstable) and produces racemic (both left and right handed versions) mixtures of nucleosides (the homochirality problem), which cannot self-assemble. In addition, the maximum spontaneous RNA assembly length of 50 mer (bases) is insufficient to code for anything meaningful (the average transcript consists of hundred to thousands of base pairs). Even assuming this problem could be solved, searches of quadrillions of randomly generated Ribonucleic acid: a chemical that directs the manufacture of proteins and sometimes codes for the genetic material within certain organisms.RNA The order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule, or the order of amino acids in a protein molecule.sequences have failed to yield a spontaneous Ribonucleic acid: a chemical that directs the manufacture of proteins and sometimes codes for the genetic material within certain organisms.RNA replicator.16
Although many of the arguments against the naturalistic origin of life may seem like God of the gaps variety, the fact that they haven't gone away after 50+ years of intensive research, but have actually increased in number, suggest that the problems are real and probably insurmountable. Multiple unattainable steps in such processes defy the laws of physics and chemistry, and cannot be explained away by promissory materialism. Originally thought to be gaps in our understanding of chemistry, origin of life research continues to produce "science of the gaps" explanations for naturalistic origin of life scenarios. Only one whose philosophy is predisposed to naturalism-only explanations would seriously entertain such unlikely scenarios as realistic models for how life arose on earth.
Design in the universe
Arguments for the presence of design in the universe consist of the unique fine tuning of the laws of physics and the uniqueness of the earth and solar system.
Law of physics
The makeup of the universe and the laws that govern how the it works are fine-tuned to an amazing degree. For example, scientists would expect in the primordial universe that the ratio of quarks to antiquarks would be exactly equal to one, since neither would be expected to have been produced in preference to the other. However, quarks outnumbered antiquarks by a ratio of 1,000,000,001 to 1,000,000,000. The remaining small excess of quarks eventually made up all the matter that exists in the universe. Without this small excess of quarks, the universe would have consisted entirely of energy, with no matter. The ratio of electrons compared to protons must be exactly equal to one to better than one part in 1037 or else electromagnetic interactions would dominate gravity, resulting in the universe consisting of scattered particles.17 The mass of the universe cannot be more than it is by one part in 1059. Based upon the mass of the universe (about 1080 baryons), adding just one extra grain of sand would have resulted in the collapse of the universe early in its history. However, none of these parameters comes close to the design required for the most recently discovered law of physics - the cosmological constant (or dark energy). This constant is fine-tuned to one part in 10120. One atheist cosmologist, confronted with these facts said, "This type of universe, however, seems to require a degree of fine tuning of the initial conditions that is in apparent conflict with 'common wisdom'."18 In conclusion, cosmology is producing more and more evidence that our universe is based upon numerous parameters that must be extremely fine tuned in order for life to exist (which is exactly opposite of what would expected if the explanation were god of the gaps). Naturalism would posit that increased knowledge in cosmology would provide evidence that our universe was just an average one, instead of an extremely unlikely one.
Design of the earth/solar system
Special Galaxy - The earth is housed in a unique spiral galaxy. Although spirals are reasonably common in the universe (~15% of all galaxies), most have been disrupted to various degrees through collisions with other galaxies. In contrast, the milky way galaxy exists within a small galaxy cluster known as the local group, being one of only two large galaxies, and has numerous, symmetric spiral arms. Scientists have yet to find a comparable galaxy among millions of others examined (see Pictures of Galaxies). The solar system exists in a space between two spiral arms, at or near the co-rotation radius, which means that it will remain between spiral arms for some time to come. In contrast, most stars in other parts of the galaxy enter and leave spiral arms periodically. Stars that travel through spiral arms risk disrupting planetary orbits through gravitational interactions with other stars. In addition, our fortuitous location between spiral arms at the co-rotation radius allows us an almost unhindered view of the universe, with the possibility that this was intentional.19
Special Solar System - Now that over 300 extrasolar planetary systems have been discovered to date, we know that our solar system is quite rare. So far, it is the only planetary system in which the large gas giants are located far (greater than 5 AU) from the parent star. In all other systems, such gas giants are found at locations within the region that would correspond to where our inner, rocky planets are located. In all other planetary systems discovered to-date, large gas giants form at a distance from their star, but migrate inward. Computer simulations indicate that this is the usual scenario, with our solar system being a rare exception.20 According to Frederic Rasio, the author of the study:
"We now know that these other planetary systems don't look like the solar system at all. We now better understand the process of planet formation and can explain the properties of the strange exoplanets we've observed. We also know that the solar system is special and understand at some level what makes it special."21
The reason why it is important to have gas giants far from the Sun is because Jupiter and Saturn protect the inner solar system from constant bombardment by comets. Without this protection, advanced life would not be possible on the earth. In addition, a large gas giant roaming close to a star's habitable zone would eject any rocky planets from the planetary system.
Special Star - Our star, the Sun, is a slightly above average-sized star. Large stars burn too quickly for life to develop on possible terrestrial-like planets (with stellar life spans as short as a few million years). Small stars burn for a long time (tens of billions of years). However, the reduced energy output requires that rocky planets be very close to the star in order to be within the habitable zone. This closeness results in all such planets becoming tidally locked (rotational period equals revolutionary period) within a short period of time. Tidal locking means that one side continually faces the star, resulting in extremely hot temperatures, whereas the other side stays very cold, eventually accumulating all the water as ice, and possibly even freezing out the atmosphere.
The Sun is unique in that it is one of only a small percentage that are metal-rich. Originally, the universe consisted almost entirely of hydrogen and helium. The first stars had no rocky planet companions, since there were no building materials. The Sun has rocky planets because it is probably a third generation star that had the fortune of igniting within an area of previous supernova events. Rocky planets cannot form at all unless the amount of metallicity is at least 60% of that of the Sun. The Sun is an unusually metal-rich star (richest out of 174 well-studied stars).22 Although planets are fairly common around stars, no earth-sized rocky planets have been discovered to date (2008). The smallest planet discovered is 5.5 times as massive as the earth, but is quite frozen.23 Part of the problem discovering rocky planets is that they had been impossible to detect with the techniques that have been used to discover large planets. However, new instrumentation and techniques developed since 2005 should allow the discovery of earth-like rocky planets within the next few years, if they exist. So, the lack of rocky planets is a God of the gaps explanation for now, but will be answered within the next few years.
Special Planet - The earth is a remarkable place among the other planets and moons of our solar system. It is the only rocky planet in our solar system that contains significant amounts of liquid water on its surface. Although the planet Mars sustained surface water billions of years ago, it was mixed with large amounts of sulfuric acid - producing toxic seas that would have made it unlikely that living organisms could have survived there.24
However, the presence of liquid water is not the only unusual feature of planet earth. Although water is quite common in the universe, it would be either absent (as it is on the other rocky planets in our stellar system) or so abundant on rocky planets that virtually all other rocky planets would be either deserts or waterworlds.25 All other rocky planets (including our "sister planet," Venus) in our solar system have no significant tectonic activity. Without tectonic activity, water-abundant planets like earth would be water worlds. The reason that earth has tectonic activity and continents is because it suffered a major collision with a Mars-sized planet soon after its formation. The metallic core of the collider was incorporated into the earth's core, with the outer part becoming earth's moon. Without this additional metallic component, earth's core, kept molten through radioactive decay, would have solidified, shutting down tectonic activity and the earth's magnetic dynamo (which protects earth's creatures from solar radiation). Large planets do not form continents because the increased gravity prevents significant mountain and continent formation. Earth-sized planets completely flood, and any land formed is eroded by the seas in a short period of time. Smaller planets lack tectonic activity, so would have no land masses, but would be completely covered with water. Therefore, virtually all rocky planets (other than those that suffered a large collision soon after formation) would be expected to be water worlds. Earth-like planets (with both water and dry land) would be extremely rare. Exactly how rare they would be in the universe is uncertain, making the argument somewhat of a God of the gaps type for now. However, the next decade should give us a much better estimation. For more information on these design features, see The Incredible Design of the Earth and Our Solar System.
Whereas a God of the gaps explanation of the design of our galaxy, solar system, and planet would posit that science would be discovering that we really aren't that unique, the data continues to show that we are more unique than first thought. In fact, some of this uniqueness was discovered just this year.20 If the data truly were God of the gaps, we would expect the evidence for design to decrease, rather than increase with additional scientific knowledge.
More Gaps
Removing the "gaps" in science
One particular "gap" in scientific understanding concerned the darkness of the night sky. Since an infinite universe would result in a sky that was always light (because the volume of space increases 8-fold with a doubling of the radius, although the amount of light decreases 4-fold with the same doubling). Despite having this knowledge since Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers first proposed it in 1823, scientists proposed the steady-state universe - infinite in age and size. Of course, it turns out that the "gap" in our understanding of why the sky was dark at night was no gap at all, but a real observation that required that the universe be non-infinite and non-eternal. So, it is not just theists who posit the existence of gaps - it is commonly done in science, as well.
Gaps in atheists' arguments
Scientists and theists are not the only ones who use "gaps" arguments. In fact, many atheists use gaps arguments to argue against the existence of God. Most of the answers on the hall of questions page merely remove the gaps in atheists' understanding - either philosophical, biblical, or scientific in nature. For example, atheists complain that a loving God would never allow evil in His creation. However, this argument is based on a gap in atheists' understanding of the main purpose of the universe - to choose between good and evil. Obviously, it would be impossible to choose good over evil if evil did not exist.
In another example, atheists cannot imagine how God can exist as a non-created being. However, the gap is filled by throwing out the assumption that time has always existed. We are so used to cause and effect that we can't imagine an existence without it. However, all the evidence from cosmology points to the fact that the universe - the dimensions of space, matter, energy, and time - all came into existence 13.7 billion years ago. The Bible indicates that God created the entire universe and the time in which it operates.26 If it is true that God created time specifically to accomplish His purposes for the universe, it isn't unreasonable to propose that God (who exists outside the universe) is uncreated. Cause and effect does not operate in the absence of time. Atheists' arguments suggesting that if God exists, He must have been created by an even greater cause fail because they ignore evidence (the gap) suggesting that time began only at the creation of the universe.
Conclusion 
Many skeptics believe that all arguments for the existence of God fall into the God of the gaps variety. According to this premise, one would expect these arguments to become fewer in number as scientists make more discoveries and learn more about our world. In reality, evidence continues to accumulate suggesting that the universe was designed by an intelligent agent. The evidence suggesting that the universe and its physical laws were designed continues to accumulate at a rapid rate. Although we are not certain about the degree to which the earth and solar system are specially designed, evidence to-date suggests that earth-like planets are rare in the universe.
Ten years ago, it was thought that neo-Darwinian evolution had eliminated all suggestion that living organisms were designed by an intelligent agent. However, recent studies in molecular biology and genetics have eliminated much of the supposed evidence that life exhibits numerous examples of poor design, including the presence of "junk DNA" (which does not exist) and pseudogenes. New genetic evidence suggests that mammalian DNA is optimally coded to reduce DNA size through overlapping transcripts. This encoding presents special problems to current Darwinian evolutionary models, since these mechanisms would be unable to produce these kinds of sequences through mutation and natural selection.
Origin of life studies continue to run into problems with uncooperative chemistry, and planetary science discoveries about the nature of early earth environments. Replicator-first models fail to establish mechanisms to produce even the basic chemical building blocks for an "RNA World", including a failure to produce homochiral sugars and amino acids. Beyond these problems, the assembly of rudimentary biological membranes under early earth environments is virtually impossible.

![]() If evidence for the existence of God were truly a God of the gaps type,
we would expect these gaps to be disappearing, instead of increasing in
number. The evidence is so strong that long-time promoter of atheism, Antony
Flew announced in 2004 that he had become a deist because he "had to go
where the evidence leads."4 His new book,
There Is a God: How the World's Most Notorious Atheist Changed His Mind
If evidence for the existence of God were truly a God of the gaps type,
we would expect these gaps to be disappearing, instead of increasing in
number. The evidence is so strong that long-time promoter of atheism, Antony
Flew announced in 2004 that he had become a deist because he "had to go
where the evidence leads."4 His new book,
There Is a God: How the World's Most Notorious Atheist Changed His Mind ![]() explains how he came to the conclusion that God does exist.
explains how he came to the conclusion that God does exist.
Related Pages 
- "Junk" DNA: Why non-coding DNA Isn't Really Junk
- Pseudogenes: Argument for Evolution and Against Design?
- Bad Designs in Biology? - Why the "Best" Examples Are Bad
- Abiogenesis: Is the Chemical Origin of Life a Realistic Scenario?
- Origin of Life: Earth's Early Atmosphere Wasn't Reducing
- Problems with the Origin of Biological Membranes in an Early Earth Environment
- Origin of Homochirality: A Major Problem for Origin of Life Theories
- Is God Real? Does Science Answer "Is There a God?"
- Evidence for the Fine Tuning of the Universe
- Extreme Fine Tuning - Dark Energy or the Cosmological Constant
- The Incredible Design of the Earth and Our Solar System
- Moons Like Earth's Moon are Rare in the Universe
- There is Too Much Evil and Suffering For God to Exist?
- If God Created Everything, Who Created God?
- The Universe is Not Eternal, But Had A Beginning
- Why is There Something Instead of Nothing?
References 
- See numerous examples in "Junk" DNA: Why non-coding DNA Isn't Really Junk.
- Spencer, Geoff and Anna-Lynn Wegener. 2007. New Findings Challenge Established Views on Human Genome. NIH News.
- See Pseudogenes: Argument for Evolution and Against Design?
- Lee, J. T. 2003. Molecular biology: Complicity of gene and A sequence of DNA that is very similar to a normal gene but that has been altered so it is not expressed.pseudogene [News and Views] Nature 423: 26-28.
- Hirotsune, S., Yoshida, N., Chen, A., Garrett, L., Sugiyama, F., Takahashi, S., Yagami, K., Wynshaw-Boris, A., and Yoshiki, A. 2003. An expressed A sequence of DNA that is very similar to a normal gene but that has been altered so it is not expressed.pseudogene regulates the messenger- Ribonucleic acid: a chemical that directs the manufacture of proteins and sometimes codes for the genetic material within certain organisms.RNA stability of its homologous coding The functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.gene. Nature 423: 91-96.
- Balakirev, E. S. and F. J. Ayala. 2003. PSEUDOGENES: Are They "Junk" or Functional DNA? Ann. Rev. Genetics 37: 123-151.
- Zheng, D. and M. B. Gerstein. 2007. The Ambiguous Boundary between Genes and Pseudogenes: The Dead Rise Up, or Do They? Trends in Genetics 23: 219-24.
- The ENCODE Project Consortium. 2007. Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature 447: 799-816.
- Makalowska, I., C.F. Lin, and W. Makalowski. 2005. Overlapping genes in vertebrate genomes. Comput. Biol. Chem. 29: 1-12.
- In a 1996 intrerview with Reuters, Miller said, "Making the amino acids made it seem like the rest of the steps would be very easy. It's turned out that it's more difficult than I thought it would be. It's a series of little tricks. Once you learn the trick, it's very easy. The problem is learning the trick."
- Watson, E. B. and T. M. Harrison. 2005. Zircon Thermometer Reveals Minimum Melting Conditions on Earliest Earth. Science 308: 841-844.
- Although it is possible that life could have arisen before 4.3 billion years ago, it would have been destroyed by 3.9 billion years ago, during the late heavy bombardment. "A few of these impactors were probably 500 kilometers in diameter--big enough to create a superheated atmosphere of vaporized rock that would in turn have vaporized the oceans for 2700 years and sterilized even the subsurface, say Sleep and Zahnle." Cited from Benner, S.A. 1999. Old views of ancient events. Science 283: 2026.
- Szathm�ry, E. 2000. The evolution of replicators. Philosophical Transactions: Biological Sciences 355: 1669-1676.
- Knauth, L.P. 2000. Life on Land in the Precambrian and
the Marine vs. Non-Marine Setting of Early Evolution. First Astrobiology
Science Conference, April 3-5, 2000, NASA Ames Research Center, 403 (Abstract
353).
Knauth, L.P. 2002. Early Oceans: Cradles of Life or Death Traps? Astrobiology Science Conference 2002, April 7-11, NASA Ames Research Center. p. 9. - See Is the Chemical Origin of Life (Abiogenesis) a Realistic Scenario?
- Benner, S.A. 1999. Old views of ancient events. Science 283: 2026.
- See Evidence for the Fine Tuning of the Universe.
- Zehavi, I, and A. Dekel. 1999. Evidence for a positive cosmological constant from flows of galaxies and distant supernovae Nature 401: 252-254 401: 252-254.
- The Bible indicates that God wanted us to see His glory
through the appearance of the universe:
"The heavens declare the glory of God; the skies proclaim the work of his hands. Day after day they pour forth speech; night after night they display knowledge. There is no speech or language where their voice is not heard. Their voice goes out into all the earth, their words to the ends of the world." (Psalm 19:1-4) - Thommes, E. W., S. Matsumura, F. A. Rasio. 2008. Gas Disks to Gas Giants: Simulating the Birth of Planetary Systems. Science 321: 814-817.
- Universally Speaking, Earthlings Share a Nice Neighborhood. National Science Foundation Press Release 08-137. August 7, 2008.
- J.-P. Beaulieu, et al. 2006. Discovery of a cool planet of 5.5 Earth masses through gravitational microlensing. Nature 439: 437-440.
- Lecture 24: Is There Other Intelligent Life in the Universe?
- Bibring, J. Y. Langevin, J. F. Mustard, et al. 2006. Global Mineralogical and Aqueous Mars History Derived from OMEGA/Mars Express Data. Science 312:400-404.
- See The Incredible Design of the Earth and Our Solar System.
- The Bible indicates that God was acting before the
creation of the time:
- No, we speak of God's secret wisdom, a wisdom that has been hidden and that God destined for our glory before time began. (1 Corinthians 2:7)
- This grace was given us in Christ Jesus before the beginning of time (2 Timothy 1:9)
- The hope of eternal life, which God... promised before the beginning of time (Titus 1:2)
- To the only God our Savior, through Jesus Christ our Lord, be glory, majesty, dominion and authority, before all time and now and forever. Amen. (Jude 1:25)
Today's New Reason to Believe
Integrating Science and Faith
- 11/05/2012 12:52 AM
Imperial College Debate on Evidence for God
In spring of 2012, my colleague Kenneth Samples and I spent several days in London, England, speaking in universities, churches, leadership gatherings, and at a conference. God gave us a wonderful opportunity to take RTB’s message of science-faith compatibility overseas. Here I recap my interactions with distinguished professor Lewis Wolpert. **** On May 24, 2012, … Read more
() - 11/01/2012 12:30 AM
Resource Highlight: Creation Day Debates
Earlier this week, guest writer Otis Graf explained how the ejection dynamics of meteoroids from the star Beta Pictoris and the meteoroids’ detection on Earth cannot be reconciled with a young universe—thus challenging young-earth proponent Dr. Jason Lisle’s model for solving the distant starlight problem. RTB’s Hugh Ross and Fazale Rana have debated Dr. Lisle … Read more
() - 10/29/2012 12:44 AM
Alien Particles Challenge a Young-Earth Creation Model
A collimated beam of meteoroids from the star Beta Pictoris has been discovered. However, the ejection dynamics at the star and the meteoroids’ detection on Earth cannot be reconciled with a young universe. This discovery directly challenges two tenets of young-earth proponent Dr. Jason Lisle’s model for solving the distant starlight problem. **** The 1950s … Read more
() - 10/25/2012 12:05 PM
TNRTB Classic: Basking in UV Radiation
On Monday, guest writer and visiting scholar Hugh Henry discussed research into the effects of radiation on the human body. Despite our fear of radiation, it seems that God has designed the human physiology to withstand a reasonable about of exposure. Check out this previous TNRTB from Fazale Rana on how our DNA reacts to … Read more
() - 10/25/2012 12:34 AM
TNRTB Classic: Basking in UV Radiation
On Monday, guest writer and visiting scholar Hugh Henry discussed research into the effects of radiation on the human body. Despite our fear of radiation, it seems that God has designed the human physiology to withstand a reasonable about of exposure. Check out this previous TNRTB from Fazale Rana on how our DNA reacts to … Read more
() - 10/22/2012 12:50 PM
“Deadly” Radiation and God’s Design
A feature article in the August 2012 issue of Scientific American trumpets a scary warning: “Deadly Rays from Clouds—Thunderstorms Give Out Powerful Blasts of X-Rays and Gamma Rays.”1 Headlines are written to grab the reader’s attention—whether or not the article’s content lives up to the hype. At the end of this particular article, the authors … Read more
() - 10/18/2012 12:26 AM
TNRTB Classic: Increased Oxygen
Earth experienced many events that brought it to the brink of becoming a barren wasteland. Two dramatic increases in the atmospheric oxygen content (2.5 and 0.8 billion years ago, respectively) resulted in mile-thick ice sheets that nearly encased the planet. Yet Earth rebounded from all these events, better prepared for the new life that arrived … Read more
() - 10/15/2012 12:17 AM
First Plants Bring Major Climate Change
RTB’s creation model posits that the change in life throughout Earth’s history reflects the work of a divine intelligence transforming a hostile-to-life planet into one capable of supporting humanity. As the environs change, so must the life. Studies of the first plant life on the continents show how the plants altered the land and atmosphere … Read more
() - 10/11/2012 12:36 AM
TNRTB Classic: Junk DNA and the Nucleoskeletal Hypothesis
A few days ago I wrote about the ENCODE project and the new recognition that, at minimum, 80 percent of the human genome consists of functional DNA elements. Despite some skeptics’ complaints that the media, creationists, and intelligent design adherents have misconstrued the ENCODE report, the project’s results stand. The human genome is not a vast … Read more
() - 10/08/2012 12:26 AM
Responding to ENCODE “Skeptics”
Recently, the ENCODE Project Consortium reported that 80 percent of the human genome consists of functional elements, major indicators of design. But some skeptics assert (loudly) that the results of the ENCODE project have been overhyped and misconstrued. In this article, I respond to the most salient points made by the ENCODE “skeptics.” The human … Read more
()
http://www.godandscience.org/apologetics/god_of_the_gaps.html
Last Modified September 11, 2008