The Evolution (NOT!) Times
| Published by Evidence for God from Science |
Volume 3, Number 1 September, 2002 |
|
|
|
||
Human Descent Descends to New Depths |
||
Modern humans hands down winners over NeanderthalsAnother critical anatomical difference has been found between Neanderthals and contemporary ancient humans. Wesley Niewoehner, an anthropologist at the University of New Mexico in Albuquerque has built 3D digital maps of the surfaces of the metacarpals, the bones that make up the palm of the hand, from Neanderthals and ancient humans. The shapes of the ends of the metacarpals reflect the kind of grip these creatures had. Niewhoehner's maps suggest that the smaller, slimmer hands of early modern humans were better suited to oblique grips - used when holding a complex tool with a handle, such as a hammer. Neanderthals, by comparison, were limited to grips as one has when holding a stone or baseball. Such a grip would have been powerful (you wouldn't want to shake hands with a Neanderthal), but not very dexterous. The anatomy of the Neanderthals would have prevented them from engaging in fine motor skills, such as carving and painting. The more sophisticated use of tools by early modern humans would have given them a great survival advantage over Neanderthals, possibly leading to the extinction of the Neanderthals. Clarke, T. 2001. Relics: Early modern humans won hand over fist. Nature. |
Another blow to multiregional evolutionary theoryThe multiregional evolutionary theory claims that humans are descended from multiple hominid forms (Neanderthals, Homo erectus, etc.). Recently, proponents of this theory have claimed that fossils show that an archaic Homo erectus from Java shared key features with living Asians and early modern humans in Australia. Their conclusion was that Asian H. erectus passed on some of its Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA to modern Australians and Asians (Science, 12 January 2001, p. 293). A recent genetic analysis of Asians, however, explodes this theory. The study, examining more than 1000 Asian men, determined that all of these men came from one source, between 35,000 and 89,000 years ago. The study is so convincing that some multiregional evolutionists have now dropped this theory. At the annual meeting of physical anthropologists in Kansas City, Missouri, one self-described "dedicated multiregionalist," Vince Sarich of the University of California, Berkeley, admitted:
Gibbons, A. 2001. Modern Men Trace Ancestry to African Migrants. Science
292: 1051-1052. |
|
Chirality still a problem for origin of lifeOrigin of life researchers are attempting to look for weak forces that might explain how life consists of left-handed A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. Often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins.amino acids and right handed sugars. Some of the "classic" mechanisms, such as circularly-polarized light from supernovae and other explosive astronomical events, have now been eliminated: "And researchers have shown that such [circularly-polarized] light can skew chemical reactions toward producing one particular chiral molecule at the expense of its twin. But supernovae and other astronomical sources would generate both the left and right spinning forms equally and so would be unlikely to produce an imbalance in organic molecules." Even these problems ignore the more fundamental problem of high radiation levels that would be produced by these astronomical sources that are incompatible with living organisms or even complex organic chemicals. The weak nuclear force is the only fundamental force that is chiral in nature, producing particles that spin in one direction upon radioactive decay. Therefore, researchers are trying to find conditions that might influence the percentage of left and right enantiomers of A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. Often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins.amino acids formed during prebiotic conditions. Recent experiments, using crystals, demonstrated chirality. At first glance, these experiments would seem to offer a naturalistic mechanism for chirality in living organisms. However, sources of positrons are not found in nature, so one would not have any kind of mechanisms for producing left-handed molecules, such as A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. Often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins.amino acids. In addition, the formation of crystals in a solution of salt is not the same as formation of enantiomers during the synthesis of chiral compounds, such as A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. Often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins.amino acids. The author of the original article readily admits, "Whether this is involved in the generation of chirality in A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. Often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins.amino acids is pure speculation." Service, R.F. 1999. CHEMISTRY: Does Life's Handedness Come From Within? Science 286: 1282-1283. Natural selection's most famous example, the peppered moth, based upon bad scienceThe "evolution" of the peppered moth, Biston betularia,
whose story is recounted in almost every textbook on evolution, now
appears to be based upon spurious data. According to the standard account,
only one version of Biston existed before the mid-19th century: a
white variety, peppered with black spots. During the Industrial Revolution
its numbers plummeted because it became easy prey for birds as it rested
on the pollution-blackened trunks of trees. In its place a mutant,
pitch-black form of the peppered moth began to thrive, as it could rest on
tree trunks without fear of being eaten. Precisely as predicted by
Darwin's theory of natural selection, this more fit mutant moth rapidly
outnumbered the white version, reaching 100 per cent levels in some
industrial areas. However, during the 1950's, naturalists discovered a
resurgence of the white variety, thought to be the result of the Clean Air
Acts. Scientists soon discovered that the white variety flourished
again well before the return of pollution-free trees, while the black type
continued to thrive in areas unaffected by industry. In addition,
experiments showed that neither variety of moth chooses resting places
best suited to its camouflage. Despite 40 years of effort, scientists have
seen only two moths ever resting on tree trunks - they never have
landed consistently on tree trunks, but hide under branches! It looks like
the evolution textbooks will have to be rewritten. Evolutionist Richard
Dawkins dismissed the new data, saying that, "nothing momentous hangs
on these experiments." |
Wanted: Origin of Life ExplanationWe will pay you $1.35 million for an explanation based upon scientific REALITY. Just include the following in your answer:
Conditions of "life"
The Origin-of-Life Foundation, Inc.�. (http://www.us.net/life/) Advertisement |
|
Having a harmful of bad effect.Deleterious A permanent structural alteration in DNA, consisting of either a substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotide bases.mutation rate too high for humans |
||
|
A recent study examined the A permanent structural alteration in DNA, consisting of either a substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotide bases.mutation rate for humans. Using "conservative assumptions" the authors found that the overall A permanent structural alteration in DNA, consisting of either a substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotide bases.mutation rates was 4.2 Permanent structural alterations in DNA, consisting of either substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotide bases.mutations per person per generation, with a Having a harmful of bad effect.deleterious rate of 1.6. When using more realistic assumptions the overall A permanent structural alteration in DNA, consisting of either a substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotide bases.mutation rate for humans become 6.7 with a Having a harmful of bad effect.deleterious rate of 3.1. Such a high rate should have resulted in extinction of our species long ago. They stated in their conclusion: "The Having a harmful of bad effect.deleterious A permanent structural alteration in DNA, consisting of either a substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotide bases.mutation rate appears to be so high in humans and our close relatives that it is doubtful that such species, which have low reproductive rates, could survive if Relating to a permanent structural alteration in DNA, consisting of either a substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotide bases.mutational effects on fitness were to combine in a multiplicative way." |
The authors must rely upon a rare association of Permanent structural alterations in DNA, consisting of either substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotide bases.mutations, termed synergistic epistasis to explain why the numerous hypothesized Having a harmful of bad effect.deleterious Permanent structural alterations in DNA, consisting of either substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotide bases.mutations have not overwhelmed our All the DNA contained in an organism or a cell, which includes both the chromosomes within the nucleus and the DNA in mitochondria.genome. Instead of postulating the obvious (that the human All the DNA contained in an organism or a cell, which includes both the chromosomes within the nucleus and the DNA in mitochondria.genome is not as old as evolution would teach), evolutionists again are relying upon the improbable to retain the evolutionary paradigm. Crow, J.F. 1999. The odds of losing at genetic roulette. Nature
397: 293-294
397: 293-294. |
|
The Adequacy of the Fossil Record: The Gaps are Real! |
||
The Adequacy of the Fossil RecordEvolutionists have used the excuse that the fossil record is not
complete enough to be an accurate representation of the history of life on
the Earth. A recent book, The Adequacy of the Fossil Record
(Donovan, S.K. and C.R.C. Paul, eds. 1998. The Adequacy of the Fossil
Record. Wiley, Chichester, UK), examined the fossil record in terms of
its completeness, bias (over and under representation of certain species
and groups of organisms), and stratigraphic range (its completeness for a
species over the entire history of its existence). Their conclusions were
that the fossil record is surprisingly complete, with about 10% of all
species that have ever lived being represented. There are some biases and
stratigraphic incompleteness in the fossil record, but these problems can
be estimated mathematically from the available data. There are many
examples of stratigraphic gaps in the fossil record, with these gaps being
the rule rather than the exception. In the past, it has been assumed that
the gaps represent incompleteness of the fossil record. The authors
suggest the "heretical" view that stratigraphic data should be
used to test the phylogenetic relationships between species rather than
assume that the relationships exist and that the fossil record is
incomplete. |
Molecular clock says eutherian mammals diverged 130 million years ago - fossils indicate 65 million years agoThe molecular clock hypothesis suggests that certain orders of eutherian mammals diverge as early as 129 million years ago (Kumar, S. and S.B. Hedges. 1998. Nature 392: 917). However, the current study indicates quite clearly (from many thousands of fossils) that nearly all the placental mammalian orders appeared suddenly at the time of the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary, 65 million years ago. Researchers analyzed the quality of the fossil record during the late Cretaceous period, and found that there were large numbers of fossils that make it extremely unlikely that eutherian mammals existed before that time. According to Dr. Foote:
Foote, M. J.P. Hunter, C.M. Janis, and J.J. Sepkoski, Jr. 1999. Evolutionary and preservational constraints on origins of biologic groups: divergence times of eutherian mammals. Science 283: 1310-1314. |
|
Species sorting = species extinctionPunctuated equilibrium is dependent upon the accumulation of Permanent structural alterations in DNA, consisting of either substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotide bases.mutations within a large population that gets "sorted" into an isolated small population that interbreeds the new Permanent structural alterations in DNA, consisting of either substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotide bases.mutations. A new study destroys this idea. Instead of becoming a new species, populations that suffer drastic reductions in numbers are characterized by decreased genetic variability and an accumulation of detrimental Functional and physical units of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.genes. This happens because normally Possessing two different forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent.heterozygous (containing 2 different Variant forms of a gene at a particular locus, or location, on a chromosome.alleles of each gene) individuals become Possessing two identical forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent.homozygous, due to inbreeding. As a result, detrimental, non-expressed, A genetic disorder that appears only in patients who have received two copies of a mutant gene, one from each parent.recessive Functional and physical units of heredity passed from parent to offspring. Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein.genes become Possessing two identical forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent.homozygous and, therefore, are expressed, resulting in a less fit population. The study examined the effect of a 35-year population decline of greater prairie chickens on their fitness and fertility. The results showed that population decline and isolation of the prairie chicken led to decreased genetic variability, reduced egg viability (from near 100% to less than 80%), and a decline of fertility rates (from 93% to 74%). Only after human intervention (which brought in genetically diverse individuals from other areas) did the population begin to recover. This study calls into serious question the punctuated equilibrium concept of species sorting. (Soul�, M.E. and L.S. Mills. 1998. No need to isolate genetics. Science 282: 1658 and Wetermeirer, R.L., J.D. Brawn, S.A. Simpson, T.L. Esker, R.W. Jansen, J.W. Walk, E.L. Kershner, J.L. Bouzat, and K.N. Paige. 1998. Tracking the long-term decline and recovery of an isolated population. Science 282: 1695.) |
No transitional brain sizes between Homo and Australopithecines
|
|
Birds Did Not Evolve From Theropod Dinosaurs! |
||
Birds are Not Dinosaurs?The results of the recent study show that the hands of the theropod dinosaurs are derived from digits I, II, and III, whereas the wings of birds, although they look alike in terms of structure, are derived from digits II, III, and IV. If birds were descended from the theropod dinosaurs, we would expect homologous structures to be derived from comparable regions. One could propose that bird wings were originally derived from digits I, II, and III, but later developed another fourth digit, while the first digit regressed. However, there is no fossil evidence that this ever happened (and would be extremely unlikely, since the bird wing was fully developed, even in Archaeopteryx). The really difficult problem for the evolutionists is that the supposed link between the dinosaurs and birds is now all but gone. There are no bird-like thecodonts from which Archaeopteryx could have descended (another missing link!). Therefore, the much-touted link between dinosaurs and birds has just evaporated. For the complete story, see the article in the science section. |
Other Problems with the Birds are Dinosaurs TheoryThere are other problems with the "birds are dinosaurs" theory. The theropod forelimb is much smaller (relative to body size) than that of Archaeopteryx. The small "proto-wing" of the theropods is not very convincing, especially considering the rather hefty weight of these dinosaurs. The vast majority of the theropods lack the semilunate wrist bone, and have a large number of other wrist elements which have no homology to the bones of Archaeopteryx. In addition, in almost all theropods, nerve V1 exits the braincase out the side, along with several other nerves, whereas in birds, it exits out the front of the braincase, though its own hole. There is also the minor problem that the theropods appeared after the appearance of Archaeopteryx.
|
|
Coordinated Stasis - What (or Who) is Coordinating it?A new theory of evolution (or lack thereof) has developed from recent studies of the fossil record. Previous studies have indicated species arose and remained unchanged for millions of years before becoming extinct or followed by the appearance of new species. This observation led to the theory of punctuated equilibrium. A recent report furthers this idea with the concept of "coordinated stasis," where entire communities of species remain unchanged for millions of years. These periods can be followed by periods when "upwards of 60% of species seem to be replaced over a period of a few hundred thousand years." Neandertals are not our ancestors!
|
Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny fraud rediscoveredThe idea that "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny" (no longer
taught as a paradigm of evolution) has recently been shown to be a fraud
by its originator, Ernst Haekel. Haekel's drawings, depicting embryos at
similar stages of development, bear little resemblance to the actual
embryos. |
|
Lucy kicked out of the human family tree
|
||
References
- Richard Hinchliffe. 1997. EVOLUTION: The Forward March of the Bird-Dinosaurs Halted? Science 278: 596.
- A. C. Burke and A. Feduccia. October 24, 1997. Developmental Patterns and the Identification of Homologies in the Avian Hand. Science 278: 666.
- Richard A. Kerr. October 24, 1997. Does Evolutionary History Take Million-Year Breaks? Science 278: 576.
- Elizabeth Pennisi. September 5, 1997. Haeckel's Embryos: Fraud Rediscovered. Science 277: 1435.
- M. Krings, A. Stone, R. W. Schmitz, H. Krainitzki, M. Stoneking, and S. P��bo. July 11, 1997. Neandertal Deoxyribonucleic acid: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms.DNA Sequences and the Origin of Modern Humans. Cell 90: 19-30.
- Kerr, R.A. 1997. Climate-Evolution Link Weakens. Science 276: 1968.
- Sharp, P.M.. 1997. In search of molecular darwinism. Nature 385: 111-112.
- Shreeve, J. 1996. New skeleton gives path from trees to ground an odd turn. Science 272: 654.
http://www.godandscience.org/evolution/news.html
Last Modified September 21, 2002
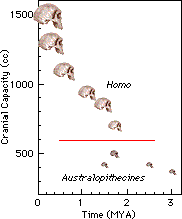 One of the problems in the theories of human evolution has been the
huge difference between the brain capacity of our genus (Homo)
and the genus of our supposed ancestors (Australopithecus). A
recent discovery of a large Australopithecine skull was anticipated to
lessen the gap between the two genera. However, a
One of the problems in the theories of human evolution has been the
huge difference between the brain capacity of our genus (Homo)
and the genus of our supposed ancestors (Australopithecus). A
recent discovery of a large Australopithecine skull was anticipated to
lessen the gap between the two genera. However, a  "Neanderthals
were not our ancestors" - a quote from the authors of the recently
published
"Neanderthals
were not our ancestors" - a quote from the authors of the recently
published  The
The 

